Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval[a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
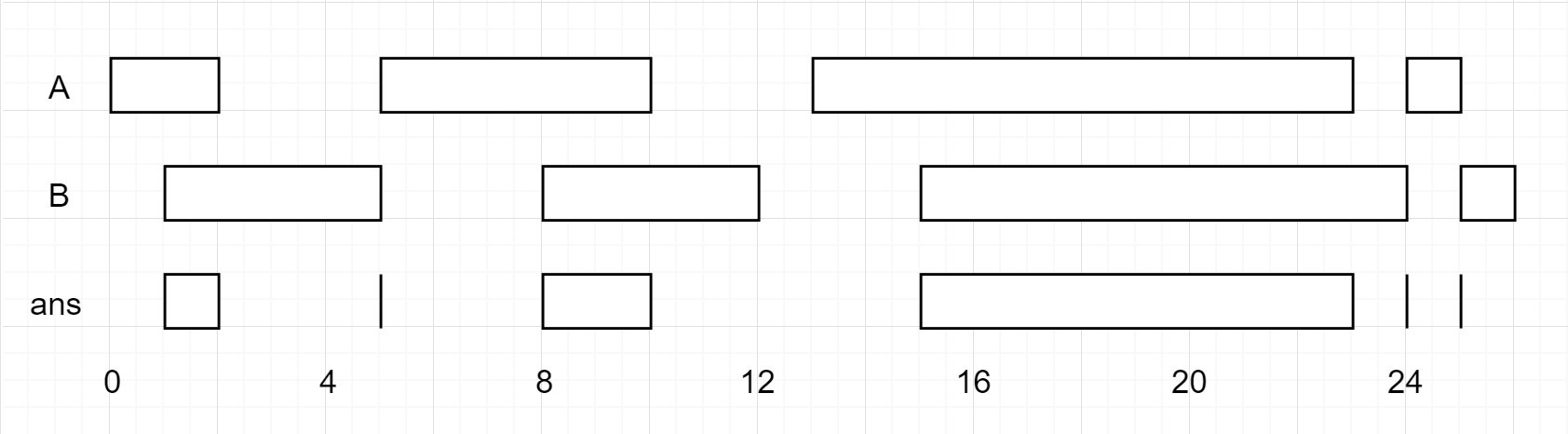
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Note:
0 <= A.length < 10000 <= B.length < 10000 <= A[i].start, A[i].end, B[i].start, B[i].end < 10^9
这道题给了两个区间数组,让返回所有相交的区间组成的数组。题目中的例子很贴心的还配了图,可以很直观的看出来相交的区间,而且可以注意到题目允许起始和结束位置相同的区间。这种类似合并区间的问题之前也做过 Merge Intervals,但是那道是只有一个区间数组进行合并,而这道题给了两个区间数组找相交区间,其实问题的本质都一样。对于这道题,由于求相交区间是要两两进行比较的,所以比较好的解法就是使用双指针来做,分别指向A和B中的某一个区间。这里用i和j两个变量表示,初始化为0,进行 while 循环,循环条件是i和j均没有遍历到末尾,然后来考虑,假如两个区间没有交集,就不用进行操作,直接平移指针即可。若i指向的区间在左边,即 A[i][1] < B[j][0] 时,i自增1,若j指向的区间在左边,即 B[j][1] < A[i][0] 时,j自增1,否则就是有交集,求交集的方法也简单,就是两个区间的起始位置中的较大值,和结束位置中的较小值组成的。将相交区间加入结果 res 后,还要平移指针,此时看,若i指向的区间结束位置小,则i自增1,若j指向的区间结束位置小,则j自增1,若二者相同,则i和j均自增1。这样循环退出后,所有的相交区间就保存在结果 res 中了,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) {
int m = A.size(), n = B.size(), i = 0, j = 0;
vector<vector<int>> res;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (A[i][1] < B[j][0]) {
++i;
} else if (B[j][1] < A[i][0]) {
++j;
} else {
res.push_back({max(A[i][0], B[j][0]), min(A[i][1], B[j][1])});
if (A[i][1] < B[j][1]) ++i;
else if (B[j][1] < A[i][1]) ++j;
else {++i; ++j;}
}
}
return res;
}
};
我们也可以再写的简洁一些,其实并不用单独处理不相交的情况,只要分别求出两个区间起始位置的较大值,和结束位置的较小值,只要当前者小于等于后者时,相交区间才存在,此时才需要加入结果 res 中,然后还是根据两个区间结束位置的大小关系来平移指针,这样的写法就简洁多了,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& A, vector<vector<int>>& B) {
int m = A.size(), n = B.size(), i = 0, j = 0;
vector<vector<int>> res;
while (i < m && j < n) {
int lo = max(A[i][0], B[j][0]), hi = min(A[i][1], B[j][1]);
if (lo <= hi) res.push_back({lo, hi});
(A[i][1] < B[j][1]) ? ++i : ++j;
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/986
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/interval-list-intersections/
https://leetcode.com/problems/interval-list-intersections/discuss/231108/C%2B%2B-O(n)-"merge-sort"
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中…)
转载请注明来源于 Grandyang 的博客 (grandyang.com),欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 grandyang@qq.com




