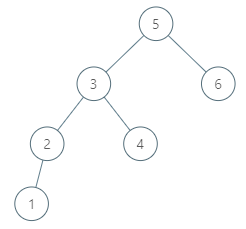
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
Example 1:
Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
null. - It’s guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
这道题让我们求二叉搜索树的某个节点的中序后继节点,那么根据 BST 的性质知道其中序遍历的结果是有序的,博主最先用的方法是用迭代的中序遍历方法,然后用一个 bool 型的变量b,初始化为 false,进行中序遍历,对于遍历到的节点,首先看如果此时b已经为 true,说明之前遍历到了p,那么此时返回当前节点,如果b仍为 false,看遍历到的节点和p是否相同,如果相同,此时将b赋为 true,那么下一个遍历到的节点就能返回了,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) {
stack<TreeNode*> s;
bool b = false;
TreeNode *t = root;
while (t || !s.empty()) {
while (t) {
s.push(t);
t = t->left;
}
t = s.top(); s.pop();
if (b) return t;
if (t == p) b = true;
t = t->right;
}
return NULL;
}
};
下面这种方法是用的中序遍历的递归写法,需要两个全局变量 pre 和 suc,分别用来记录祖先节点和后继节点,初始化将他们都赋为 NULL,然后在进行递归中序遍历时,对于遍历到的节点,首先看 pre 和p是否相同,如果相同,则 suc 赋为当前节点,然后将 pre 赋为 root,那么在遍历下一个节点时,pre 就起到记录上一个节点的作用,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) {
if (!p) return NULL;
inorder(root, p);
return suc;
}
void inorder(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *p) {
if (!root) return;
inorder(root->left, p);
if (pre == p) suc = root;
pre = root;
inorder(root->right, p);
}
private:
TreeNode *pre = NULL, *suc = NULL;
};
再来看一种更简单的方法,这种方法充分地利用到了 BST 的性质,首先看根节点值和p节点值的大小,如果根节点值大,说明p节点肯定在左子树中,那么此时先将 res 赋为 root,然后 root 移到其左子节点,循环的条件是 root 存在,再比较此时 root 值和p节点值的大小,如果还是 root 值大,重复上面的操作,如果p节点值,那么将 root 移到其右子节点,这样当 root 为空时,res 指向的就是p的后继节点,参见代码如下:
解法三:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) {
TreeNode *res = NULL;
while (root) {
if (root->val > p->val) {
res = root;
root = root->left;
} else root = root->right;
}
return res;
}
};
上面那种方法也可以写成递归形式,写法也比较简洁,但是需要把思路理清,当根节点值小于等于p节点值,说明p的后继节点一定在右子树中,所以对右子节点递归调用此函数,如果根节点值大于p节点值,那么有可能根节点就是p的后继节点,或者左子树中的某个节点是p的后继节点,所以先对左子节点递归调用此函数,如果返回空,说明根节点是后继节点,返回即可,如果不为空,则将那个节点返回,参见代码如下:
解法四:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) {
if (!root) return NULL;
if (root->val <= p->val) {
return inorderSuccessor(root->right, p);
} else {
TreeNode *left = inorderSuccessor(root->left, p);
return left ? left : root;
}
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/285
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中…)
转载请注明来源于 Grandyang 的博客 (grandyang.com),欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 grandyang@qq.com