On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j).
Now we view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3 dimensional figure to a 2 dimensional plane.
Here, we are viewing the “shadow” when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
Input: [[2]]
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation:
Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
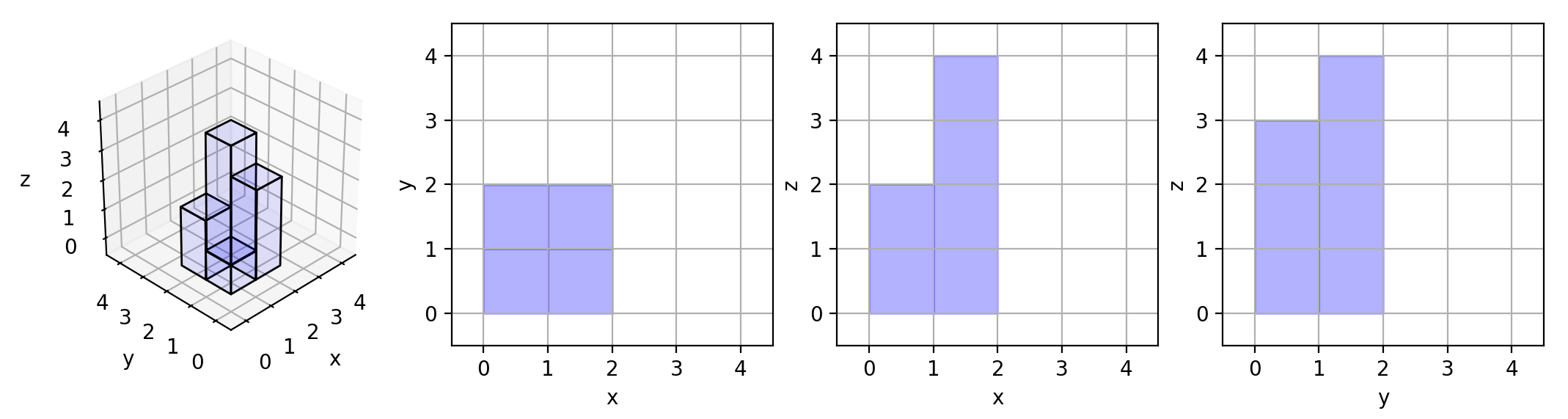
Example 3:
Input: [[1,0],[0,2]]
Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 14
Example 5:
Input: [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
Output: 21
Note:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
这道题给了我们一个二维数组 grid,用来表示一个 3D 物体形状,表示方法是 grid[i][j] 表示在 (i, j) 位置上的高度,就像垒积木一样,累出了一个三维物体。然后让我们计算三个方向的投影面积之和,所谓的三个方向分别是上方 Top,前方 Front,和侧方 Side。用过一些三维建模软件(例如 Maya, 3DMax)的同学,对这个应该不陌生。我们先来考虑正上方投影面积如何计算,由于题目中说了 grid 数组的宽和高相等,那么上方投影就是一个正方形,前提是每个 grid[i][j] 的值都大于0的话。因为若 grid 数组中有0存在,则表示正方形投影会缺少了一块。由于这个大的正方形投影是由 nxn 个小的正方形组成,那么实际上我们只要统计出小正方形的个数,那么大正方形投影的面积也就知道了(是不有点微积分的感觉)。所以我们在遍历的过程中,只要判断若 grid[i][j] 大于0,则结果 res 自增1即可。下面再来考虑另外两个方向的投影怎么计算,另两个方向的投影的可能是不规则图形,参见题目中给的那个图,如果仔细观察的话,其投影图像的每个阶段的高其实就是各行或各列中的最大值,这也不难理解,就像城市中耸立的高度不同的大楼,若要描出城市的轮廓,那么描出来的肯定都是每个位置上最高建筑物的轮廓。那么问题就变成了累加各行各列的最大值。我们实际上在一次遍历中就能完成,使用了一个小 trick,那就是在第二层 for 循环中,行最大值 rowMax 就是不断用 grid[i][j] 来更新,而列最大值 colMax 就是不断用 grid[j][i] 来更新,巧妙的交换i和j,实现了目标。然后分别把更新出来的行列最大值加到结果 res 中即可,参见代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid[0].size(), res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int rowMax = 0, colMax = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) ++res;
rowMax = max(rowMax, grid[i][j]);
colMax = max(colMax, grid[j][i]);
}
res += rowMax + colMax;
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/883
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中…)
转载请注明来源于 Grandyang 的博客 (grandyang.com),欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 grandyang@qq.com




