Given a m x n matrix mat and an integer threshold, return the maximum side-length of a square with a sum less than or equal to threshold or return 0 if there is no such square.
Example 1:
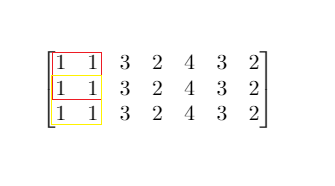
Input: mat = [[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2]], threshold = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The maximum side length of square with sum less than 4 is 2 as shown.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2]], threshold = 1
Output: 0
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3000 <= mat[i][j] <= 1040 <= threshold <= 105
这道题给了一个 m by n 的二维数组和一个整型数 threshold,让返回最大正方形的边长,使得正方形区间内的数字之和小于等于 threshold。像这种求二维数组子区间和的问题,可以很容易联想到一维数组的求子数组之和的问题,通过建立累加和数组可以快速的求出一维数组中任意区间的子数组之和。对于二维数组也是一样的道理,可以建立二维的累加和数组,然后遍历每一个正方形区间,通过累加和数组快速得到其数字之和,然后比较若小于等于 threshold,则用其边长来更新结果 res 即可。二维累加和数组的大小要比原数组大1,这样方便处理越界的问题,累加的方法就是当前位置对应的原数组的数字,加上累加数组上方和左边的数字,减去左上方的数字。
构建完成了累加和数组之后,就可以遍历所有的正方形区间了。由于只需要一个顶点和边长就可以唯一的确定一个正方形区间,所以可以遍历数组中的每一个位置,当作正方形区间的左上顶点,然后遍历所有不越界的边长,并快速求区间和。注意求区间和的方法和求累加和数组的方法是有一些区别的,当正方形区间的左上顶点为 (i, j),边长为 k+1 的时候,则右下顶点为 (i+k, j+k),区间和的计算方法是 sums[i + k][j + k] - sums[i - 1][j + k] - sums[i + k][j - 1] + sums[i - 1][j - 1],可以自行比较下和计算累加和数组的区别,然后就是和 threshold 比较了,若小于等于 threshold,则用 k+1 来更新结果 res 即可,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int maxSideLength(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int threshold) {
int res = 0, m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> sums(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
sums[i][j] = mat[i - 1][j - 1] + sums[i - 1][j] + sums[i][j - 1] - sums[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; (i + k) <= m && (j + k) <= n; ++k) {
int total = sums[i + k][j + k] - sums[i - 1][j + k] - sums[i + k][j - 1] + sums[i - 1][j - 1];
if (total <= threshold) res = max(res, k + 1);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
由于所求的最大边长是有范围的,最小为0,最大不超过m和n中的较小值,那么就可以用二分搜索法来增加查找的速度。还是需要建立累加和数组 sums,然后就可以开始二分搜索了,这里用到的二分法是博主之前的总结帖 LeetCode Binary Search Summary 二分搜索法小结 中的第四类,用子函数当作判断关系(通常由 mid 计算得出)。判断的子函数其实就是在整个数组中查找是否存在均有给定边长的正方形区间,使得其数字和小于等于 threshold。因为此时边长确定了,只要遍历左上顶点的位置,然后通过累加和数组快速计算出区间和进行判断即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int maxSideLength(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int threshold) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(), left = 0, right = min(m, n);
vector<vector<int>> sums(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
sums[i][j] = mat[i - 1][j - 1] + sums[i - 1][j] + sums[i][j - 1] - sums[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (squareExisted(sums, threshold, mid)) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return right;
}
bool squareExisted(vector<vector<int>>& sums, int threshold, int len) {
for (int i = len; i < sums.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = len; j < sums[0].size(); ++j) {
if (sums[i][j] - sums[i - len][j] - sums[i][j - len] + sums[i - len][j - len] <= threshold) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
再来看一种更加高效的方法,这种方法在建立累加和的过程中就直接进行判断了,而且每次只判断是否有比当前已经存在的正方行边长大1的区间,有的话就让结果 res 自增1,因为左上顶点一次只能移动一个位置,不管是向右,还是向下移动,边长最多也只能增加1。这道题的难点还是在于计算区间时下标的转换,因为此时的正方形区间的右下顶点为 (i, j),左上顶点为 (i-res, j-res),计算区间和的方法为 sums[i][j] - sums[i - res - 1][j] - sums[i][j - res - 1] + sums[i - res - 1][j - res - 1],前提要保证 i - res - 1 和 j - res - 1 均大于等于0,以防止越界,参见代码如下:
解法三:
class Solution {
public:
int maxSideLength(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int threshold) {
int res = 0, m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> sums(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
sums[i][j] = mat[i - 1][j - 1] + sums[i - 1][j] + sums[i][j - 1] - sums[i - 1][j - 1];
if (i - res - 1 >= 0 && j - res - 1 >= 0 && sums[i][j] - sums[i - res - 1][j] - sums[i][j - res - 1] + sums[i - res - 1][j - res - 1] <= threshold) {
++res;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/1292
参考资料:
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中…)
喜欢请点赞,疼爱请打赏❤️.
微信打赏
 |
|
Venmo 打赏

—|—
转载请注明来源于 Grandyang 的博客 (grandyang.com),欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 grandyang@qq.com




