We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You’re given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
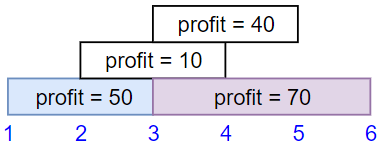
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70]
Output: 120
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job.
Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
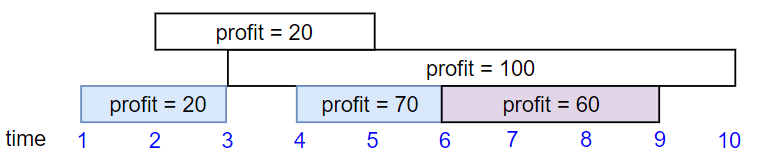
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60]
Output: 150
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job.
Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
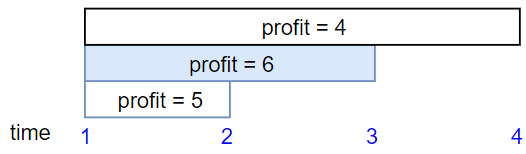
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4]
Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 10^91 <= profit[i] <= 10^4
这道题说是给了n个工作,每个工作的起始时间,结束时间,和利润分别放在对应的三个数组里面,要求每个时间点只能做一份工作,问可以得到的最大利润是多少。这是一道典型的背包问题 Knapsack Problem,对于此类问题,动态规划 Dynamic Programming 就是不二之选。首先来定义 DP 数组,这里要求的是在某个时间段内的最大利润,但并没有给定具体的结束时间,所以这里用一个映射比较合适,同时我们还希望保持时间的顺序,则可以用一个 TreeMap 来建立结束工作的时间和所获得的利润之间的映射,初始化时将 {0, 0} 的映射对儿加入,后面会解释原因。由于给定的工作可能是乱序的,这样不利于知道某个时间段内的所有工作,需要按照结束时间给所有工作排个序,为啥是结束时间呢?因为只有某个工作在给定的时间内结束了,才可以获得该工作的利润。题目中将起始时间,结束时间,和利润放到了三个不同的数组中,这里新建一个二维数组,将同一个工作的三个信息放到一起,将结束时间放到第一个,因为要根据其进行排序。
按结束时间排好序了之后就可以开始遍历所有工作了,对于遍历到的工作,就需要采用类似背包问题的更新方法了,若不干这份工作,什么都不用更新,若干了这份工作,那么跟这份工作时间冲突的其他的工作就不能干了,这份工作的起始时间已知,只要在该起始时间之前找到一个最大的利润值,再加上当前工作的利润,若整体的利润值最大,就可以用更新当前工作结束时间的 dp 值。用二分搜索法来进行查找可以提高效率,在 C++ 中使用 upper_bound 来查找第一个大于目标值的数,然后向前退一位,就是第一个小于等于目标值的数了,由于这里需要退位操作,为了防止越界,所以初始化时提前加入了 {0, 0} 的映射对儿。找到之前的最大利润后,加上当前工作的利润值,若这个总利润值大于最后的时间点的 dp 值时,更新当前工作结束时间的 dp 值。因为最终希望整体的利润最高,所以每次需要跟最后时间点的 dp 值进行比较,参见代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<vector<int>> jobs;
map<int, int> dp{{0, 0}};
for (int i = 0; i < startTime.size(); ++i) {
jobs.push_back({endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i]});
}
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
for (auto &job : jobs) {
int cur = prev(dp.upper_bound(job[1]))->second + job[2];
if (cur > dp.rbegin()->second) dp[job[0]] = cur;
}
return dp.rbegin()->second;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/1235
类似题目:
Maximum Earnings From Taxi
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/discuss/409188/C%2B%2B-with-picture
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中…)
喜欢请点赞,疼爱请打赏❤️.
微信打赏
 |
|
Venmo 打赏

—|—
转载请注明来源于 Grandyang 的博客 (grandyang.com),欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 grandyang@qq.com




